RSA Algorithm With Examples
RSA Algorithm
The RSA algorithm (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is the basis of a cryptosystem -- a suite of cryptographic algorithms that are used for specific security services or purposes -- which enables public key encryption and is widely used to secure sensitive data, particularly when it is being sent over an insecure network, such as the internet.
Public key encryption algorithm:
RSA algorithm is an asymmetric cryptography algorithm. Asymmetric actually means that it works on two different keys i.e. Public Key and Private Key. As the name describes that the Public Key is given to everyone and the Private key is kept private.
The Public key is used for encryption, and the Private Key is used for decryption. Decryption cannot be done using a public key. The two keys are linked, but the private key cannot be derived from the public key. The public key is well known, but the private key is secret and it is known only to the user who owns the key. It means that everybody can send a message to the user using user's public key. But only the user can decrypt the message using his private key.
The Public key algorithm operates in the following manner:
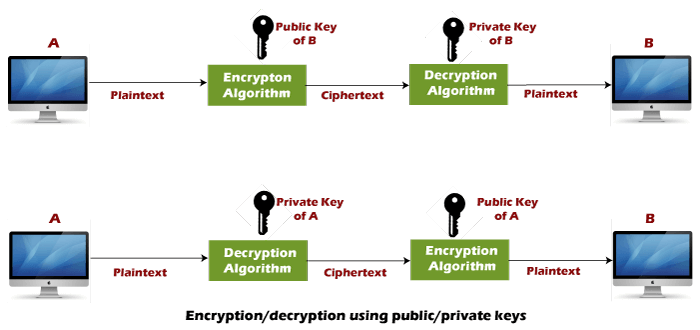
- The data to be sent is encrypted by sender A using the public key of the intended receiver
- B decrypts the received ciphertext using its private key, which is known only to B. B replies to A encrypting its message using A's public key.
- A decrypts the received ciphertext using its private key, which is known only to him.
RSA encryption algorithm:
RSA is the most common public-key algorithm, named after its inventors Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA).
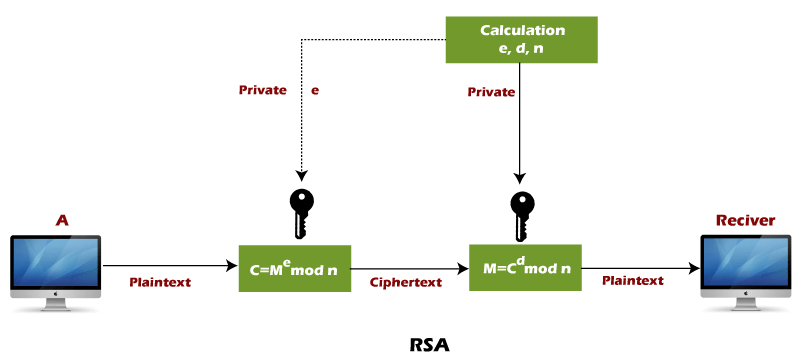
RSA algorithm uses the following procedure to generate public and private keys:
- Pick two large primes p, q
- Compute n= p * q and Φ(n)= (P-1) (Q-1)
- Choose a public key e such that 1<e<Φ(n) gcd(e,Φ(n))=1
- Calculate d such that d= (1+k * Φ(n))/e
- Let the message key be M
- Encrypt: Me mod N
- Decrypt: Cd mod N
Comments
Post a Comment